Observation of Metal Surface Structure
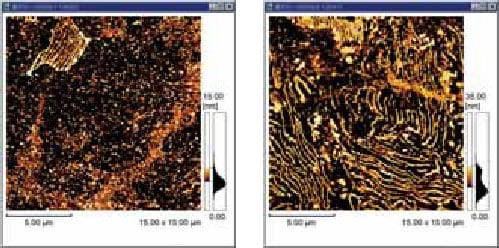
S25C Carbon Steel (After Nital Processing) S55C Carbon Steel (After Nital Processing)
The differences in carbide dispersion between two structural materials of differing carbon concentrations, S55C (carbon concentration of 0.55%) and S25C (carbon concentration of 0.25%), were observed. As pretreatment, the materials were buffed and then immersed in performed1.5% nital solution in order to create microscopic level differences. In the material with the higher carbon concentration, S55C, many areas with a laminated perlitic structure, where the ferrite phase (γFe) has corroded and the cementite phase (Fe3C) has come to the fore, were observed.

Observation of Metal Surface Structure with SEM
The surface structure of metals is also observed using optical microscopes and SEMs. SPMs, however, yield 3D data and can therefore be used to analyze the depth of corrosion.
In order to withstand metal fatigue and destruction, the structures of ferrous materials are very intricate and complex. It is expected that the SPM, which facilitates high-magnification observation, will be used more widely in fields that have been handled with the SEM and TEM until now.
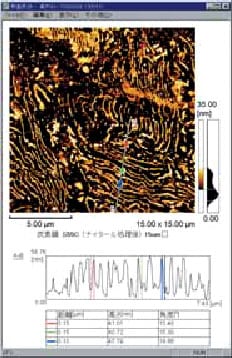
Example of Cross-Section of Metal Surface Structure Analyzed with SPM


