AFM Observation of a Living Cell
Introduction
An optical micscope or a scanning electron microscope (SEM) has been used so far fo the observation of cells, but SEM permits observation of cells after pre-treatment like fixation or dehydration before observation, instead of observ ing living cells in situ. For that reason, it required time for pretreatment and deformation of the cells was inevitable by such pretreatment.
In case it is possible to observe living cells in situ, it may not only contribute to saving labor in sample pretreatment, but it may prevent deformation of the sample due to pretreatment, enabling image of the cells more closer to those in the living condition.
Introduced here is a trial of observing living cell in situ by making use of a function of AFM which permits observation of a cell in solution. The image of the cell thus obtained was compared with the observation of cells that were treated by conventional fixation and drying ; as a result, it has been revealed that by the conventional method, shrink of the sample occurs, and that it is worthwhile to observe the living cells in situ.
AFM Observation of a Cell in a Solution
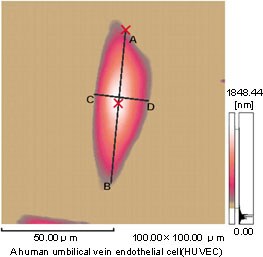
Fig.1(a) AFM Observation of a Living Cell
Shown in Fig.1 (a) is a cultured endothelial cell of the human umbilical artery caught by contact mode of AFM in a solution spiked with a culture solution. This cell was cultured in a culture medium containing cow’s fetal serum on the cover glass, and was directly put into a solution cell of the AFM without being exposed to the air, and was observed by the AFM. The solution cell was filled with a basic culture medium in which the cell was allowed to freely continue its activity. As a result, it was observed as a beautiful image unavailable before.
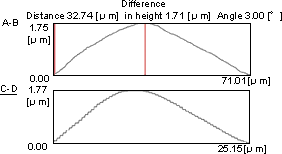
Fig.1(b) Cross Section Measurement of a Cell
Fig.1 (b) shows cross section measurement of a cell. By analyzing the 3D data, it was revealed that the size of the cell body (with skirt area around the nucleus removed) was 71μm × 25μm, and the height 1.75μm. It is comprehended from the data that the rising angle in the longitudinal direction is 3.0°.
Fig.1 (c) is a 3D display of (a), in which the entire image of endothelial cell is presented in good image.
Based on the 3D data, free image display that is not attained by SEM.
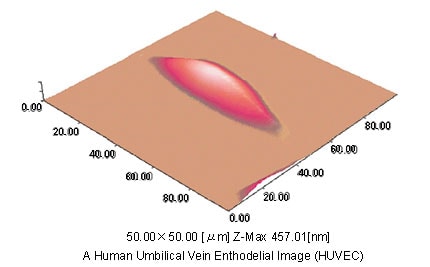
Fig.1(c) A 3-Dimensional Image
AFM Observation of a Cell in the Air after Treatment
A cultured cell put on the cover glass was fixed for 2 hours in the presence of glutaraldehyde, then dried quickly in the air and was observe by AFM. Affected by fixation or drying in the air, the cell apparently deformed with fine undulation appearing on the surface. The height of the cell was as low as 457nm maximum. In comparison with the cell in Figure 1, the cell squeezed to 1/4, revealing the problem with the previous method of observation.
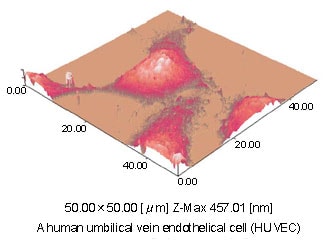
Fig.2 AFM Observation of a Cell after Treatment
*Umbilical Vein :
Two arteries and one vein are connected to the umbilical cord of human. For the separation of endothelial cell, this vein having a large diamter is often used. Informed consent has been obtained for the use of this sample
Data :
By courtesy of Professor Sugimoto and Takemasa, Anatomy Seminar No.1, Nippon Medical Cllege.


